Purpose-built pharmaceutical refrigerators are specialised cold-storage equipment designed for the safe storage of medicines and healthcare products. Pharmaceutical refrigeration needs to ensure that medicines and vaccines are retained at their optimum temperature to keep them safe and effective for use.
Pharmaceutical refrigeration equipment has to maintain precise, temperature conditions, minimising the risk of deterioration and contamination. Pharmaceutical refrigeration guidelines to ensure the proper storage of medicinal products are issued by the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulator Agency (MHRA) and the General Pharmaceutical Council (GPhC).
In this guide, we explore essential aspects of pharmaceutical refrigeration, including how to select the right equipment, installation, and maintenance.
The features of a pharmaceutical refrigerator
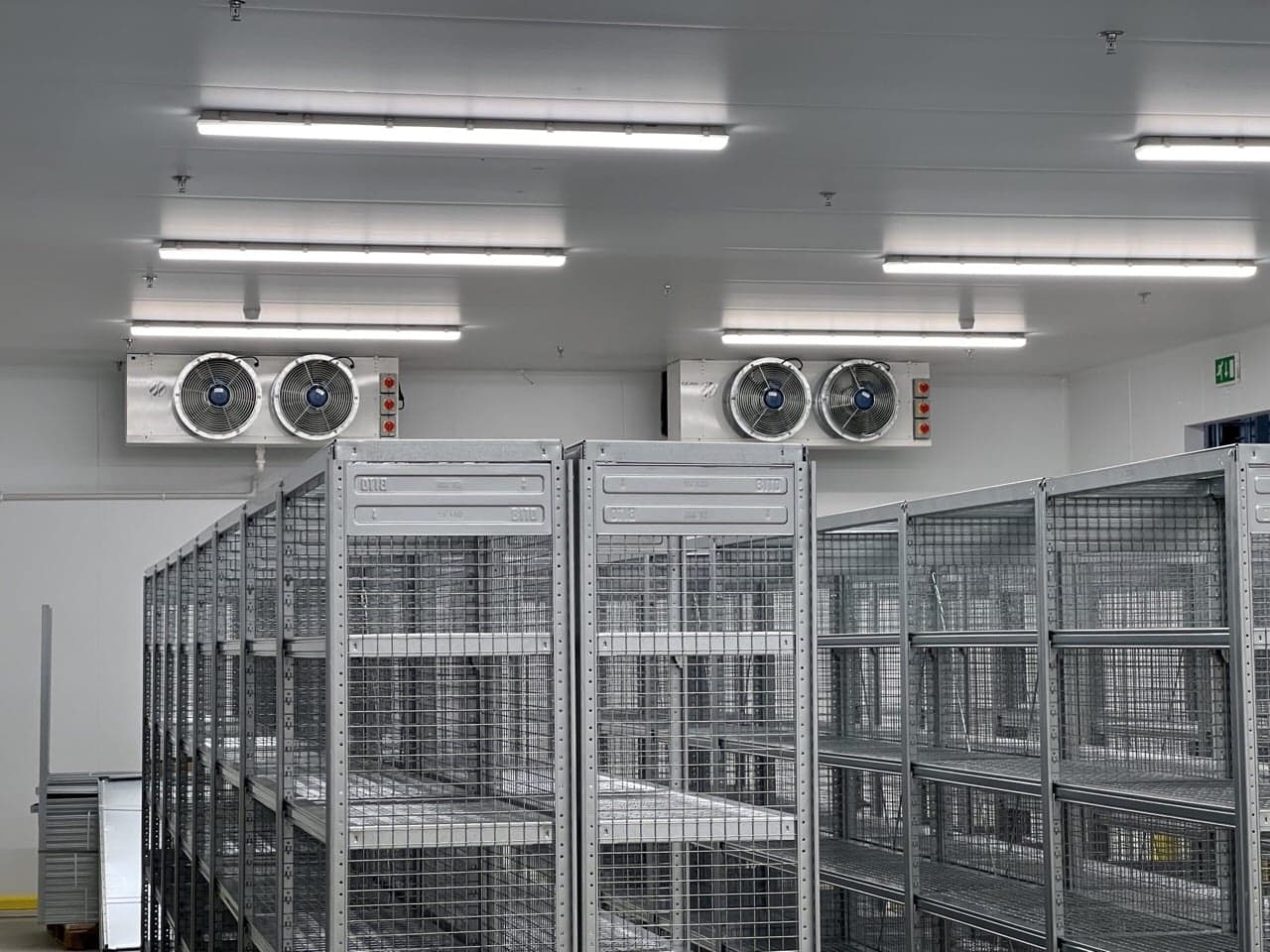
Pharmaceutical refrigeration equipment is significantly different from domestic or standard commercial refrigerators in both their design and function.
Pharmaceutical refrigerators will typically include a range of key features to ensure the safe storage of medicines, vaccines, and other medical products.
These features will include:
-
Temperature Control and Stability
Pharmaceutical refrigeration equipment needs to provide sensitive temperature control and reliability. This will typically be between +2°C and +8°C, with very minimal fluctuations that could damage the products being stored. Pharmaceutical refrigeration will usually be equipped with digital thermostats and advanced cooling systems to prevent sudden spikes in temperature.
-
Alarm Systems
Because of the consequences of temperature fluctuations, pharmaceutical refrigeration equipment will often have an integrated alarm system. These alert users to any sudden temperature deviations, power failures, or if the door has been left aside.
Some pharmaceutical refrigeration installations will include remotion monitoring and notification capabilities.
-
Air Circulation and Fan Systems
Air circulation is essential within pharmaceutical refrigerators ensuring that hot or cold spots cannot develop. These can be detrimental to the correct storage of medicinal products, so to ensure air circulation, pharmaceutical refrigeration equipment will usually include air fan systems.
-
Locking Mechanisms and Security
It is a regulatory requirement for pharmaceutical refrigeration to be fitted with locking mechanisms to ensure the security of the products it contains. Access control systems are often fitted to ensure that only authorised personnel can enter. This is crucial for protecting against unauthorised access and potential tampering.
-
Effective Internal Storage
Pharmaceutical refrigeration installations need to be functional and well-organised, ensuring that products can be located quickly. To facilitate this, thought needs to be given to internal storage. This will usually mean adjustable shelving to accommodate different packaging sizes and types. Clear labelling and compartmentalisation for easy organisation and retrieval of products is required.
-
Compliance with UK Standards
Any pharmaceutical refrigeration installation must adhere to UK regulations. This includes the MHRA’s Good Distribution Practice (GDP guidelines and the GPhC’s requirements for pharmacy storage. These standards are designed to ensure uniformity across pharmaceutical settings, as well as the quality of the products being stored, and the safety of consumers.
Pharmaceutical refrigeration will often carry certifications such as BS EN 60079-0 or ISO 13485.
Typical storage practices in pharmacy fridges
A range of careful storage practices is required to ensure the safety and efficacy of medicines, vaccines, and biological products. Temperature fluctuations, and improper storage can lead to reduced efficacy of medicines, sometimes even rendering them unsafe to use.
There are a number of best practices that should be followed to ensure that pharmaceutical products remain in optimal condition:
-
Organised storage layout
It’s vital that pharmaceutical refrigeration equipment has a well-organised storage layout. This is to ensure free airflow and the maintenance of a consistent temperature through the refrigeration unit. Medications should be arranged systematically, avoiding congestion and variations in temperature. The fridge shouldn’t be overfilled to avoid obstruction airflow that can create pockets of uneven temperatures. This can lead to potential degradation of medicines.
Different types of pharmaceutical products should be stored separately, minimising the risk of cross-contamination. Different products, such as medicines and vaccines, should each have their own designated areas within the refrigerator. These should be clearly defined and labelled to maintain order and prevent mix-ups.
-
Correct placement of item
It’s critical that pharmaceutical products are carefully placed within the refrigerator. This not only prevents mix-ups; it also helps to maintain their efficacy. Products should be kept away from walls, cooling vents, and the back of the fridge to prevent freezing. This can irreversibly damage some medications.
Temperature-sensitive products, such as vaccines, will typically be stored on the middle shelves, where temperature stability is highest. Everyday items that need to be accessed should be stored in easily accessible locations within the main compartments to minimise any disturbances to the internal temperature.
-
Labelling and expiry monitoring
To ensure proper stock management, all pharmaceutical products need to be carefully and clearly labelled with essential information. Typically, this will include the name of the medication, batch number, and expiry date. This practice not only helps with easy identification but also ensures regulatory compliance.
A first-expiry, first-out (FEFO) system should be implemented, with older stock being removed before new stock is introduced. Regular inventory checks should be carried out, removing expired or nearly expired products. Staff need to be trained in how to use this system and should understand why it is important.
-
Effective temperature monitoring
Temperature monitoring is a fundamental aspect of effective pharmaceutical storage. The use of continuous temperature data loggers and min/max thermometers might be used to ensure that storage conditions remain within the recommended range. The refrigerator’s temperature should be checked and recorded at least twice daily. Any deviations will need to be addressed quickly.
Accurate record-keeping through temperature logs is crucial for compliance with regulatory audits. These should be kept secure and be accessible for review when required. Refrigerator units will also need to be equipped with alarm or alert systems that quickly notify staff in case of temperature fluctuations.
-
Handling temperature fluctuations
Despite precautions, temperature fluctuations can still occur due to human error, equipment failure, and power outages. Having clear guidelines about how these will be handled is critical.
Immediate action is required to mitigate the potential damage, with any temperature fluctuation documented in detail. This should include the time, duration, and temperature range of the fluctuation.
Some medications may be stable enough to allow them to remain effective despite temperature deviations. Others may need to be discarded. Affected stock should be marked and segregated until further guidance is received.
Temperature monitoring guidelines
Monitoring and maintaining correct storage temperatures are essential to safeguard product safety and to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
There are a number of guidelines that should be followed to maintain the integrity of stored pharmaceuticals to ensure that they remain effective for patient use.
-
Recommended temperature ranges
To preserve the efficacy of vaccines and medicines, they need to be stored at the correct temperature. To prevent degradation, most refrigerated medicines and vaccines should be stored within a temperature range of +2°C to +8°C. Even very brief exposure to temperatures outside this range may compromise the effectiveness of the product.
Some pharmaceuticals will require freezing conditions for optimal storage, with freezers maintaining temperatures between -15°C and -50°C, depending on the specific product.
Manufacturer guidelines will determine the precise storage conditions for each vaccine or medication.
-
Daily temperature checks
As discussed above, temperature monitoring should be conducted at least twice daily to ensure that storage units remain within the designated range. Records should be maintained in a temperature logbook or with a digital monitoring system to track trends, and to identify any anomalies.
Digital temperature monitoring systems may include alert notifications for out-of-range temperatures, allowing staff to take immediate corrective action.
-
Temperature mapping and calibration
Temperature mapping involves assessing the variations in the internal temperature within storage units to ensure that cold air is distributed evenly. This process is particularly important in large refrigerators and pharmaceutical warehouses, where inconsistencies in airflow can quickly lead to temperature fluctuations. Temperature mapping will usually be conducted at least annually, or when new equipment is installed.
All temperature sensors and thermometers need to be calibrated yearly to maintain accuracy.
This calibration ensures that readings remain precise, reducing the risk of storing pharmaceuticals at incorrect temperatures. Monitoring devices need to be carefully selected for reliable readings.
-
Alarm testing and power backup plans
Power outages and equipment failure can pose a significant risk to pharmaceutical storage.
Backup power solutions or alternative storage locations can help to reduce the risk. Staff should understand any contingency plans and should know how to transfer pharmaceuticals to a safe location during an emergency.
-
Staff training
Any healthcare and pharmacy staff with responsibility for handling refrigerated medicines must receive comprehensive training.
This will typically include:
- Proper use of thermometers and digital monitoring systems.
- How to record and interpret temperature logs.
- Identifying and responding to temperature fluctuations.
- Emergency procedures in case of fridge failure or temperature excursions. Assigning a temperature monitoring officer within the team can help to ensure continuous compliance with guidelines.
- Corrective actions for temperature fluctuations
The corrective action that needs to be taken when a temperature fluctuation occurs should be clearly set out and understood by employees.
The fluctuation/deviation should be identified and documented, including time, duration, and degree of deviation. The manufacturer stability data should detail the impact of temperature fluctuation on stored pharmaceuticals. Affected products should be isolated and then marked for further evaluation.
The cause of the temperature fluctuation should be identified and measures taken to ensure that it doesn’t recur.
- Audits and compliance checks. Periodic audits should be conducted to verify that temperature monitoring procedures are being adhered to. Audits should typically include:
- Reviewing temperature logs for completeness and accuracy.
- Checking calibration records of monitoring devices.
- Ensuring compliance with alarm testing and backup power plans.
- Evaluating staff training effectiveness and knowledge retention.
Comprehensive temperature monitoring guidelines can help to safeguard the safety and efficacy of stored pharmaceuticals, as well as compliance with health and safety regulations.
Pharmaceutical refrigeration solutions from ICE
Pharmaceutical refrigeration equipment is available in a range of different sizes and configurations. At ICE, the pharmaceutical and healthcare industry is a core part of our business. We understand the high standards required, as well as providing a rapid response to breakdowns of product related equipment.
ICE can undertake the design and implementation of the whole turnkey solution of your project, from the building of the insulated enclosure itself and refrigeration systems to maintain the required temperatures, right through to the lighting, man trapped alarms and door automation.
We also provide a range of pharmaceutical refrigeration solutions for warehouse cooling.
We provide a comprehensive, regulatory compliant, maintenance service for pharmaceutical refrigeration equipment. We also offer a 24/7 emergency response service in the event of a breakdown.
Contact us to find out more about pharmaceutical refrigeration installation and maintenance you can rely upon.